acondas NEXT®: Top-down or bottom-up, waterfall or agile? Choose the right approach for your action plan.
Action plans can have very different objectives: improving effectiveness and efficiency, reducing costs or capital commitment, increasing sales, quality or employee satisfaction. But all these programmes have one thing in common: implementing them requires taking an array of actions.
These actions plans can in general be realized in two different ways:
The top-down approach was most common in the past. In this approach, optimization targets and levers for improvements are set centrally – often by top management, while implementation is handled by the line function in sequential steps.
Based on our experience,however, a decentralized and more agile bottom-up approach can deliver better and faster results in certain situations – especially when unexpected, creative solutions are welcome and well-qualified and committed employees want to support the programme. Employees often identify more closely with action plans that they or their colleagues conceive and develop, and implement them more consistently and faster.

Our acondas NEXT® method is applicable for both approaches. It combines stringent project management and early change management to achieve fast and sustainable results.
The agile procedure follows five basic steps. First, in the strategy development step, a vision is defined which serves as a basis for the further agile steps of the project teams. This includes determining a baseline centrally to support later evaluation of actions, collecting improvement ideas and approaches in the individual operative units based on a brief analysis, and prioritizing the ideas into a structured list called “product backlog”. Then, in the action evaluation step, the operational units evaluate the individual actions in the backlog in detail in a sequence of “sprints”, recording their potential target contribution and risks in a standardised evaluation sheet. At the end of each sprint, all fully detailed and evaluated proposed actions are submitted to a decision-making body for approval. In the action planning step, the implementation steps and prerequisites for approved actions are planned in further sprints, reducing the product backlog successively from sprint to sprint as the action program is built up. As soon as the implementation of an action has been fully planned, either the project team itself or, to achieve potentially greater speed, an implementation team from the line is immediately tasked with starting to implement the action. Sometimes several measures are bundled to leverage synergy effects or to implement complex change projects. While the team responsible for implementation independently follows up on the implementation steps, the final step, effect controlling, is carried out centrally.
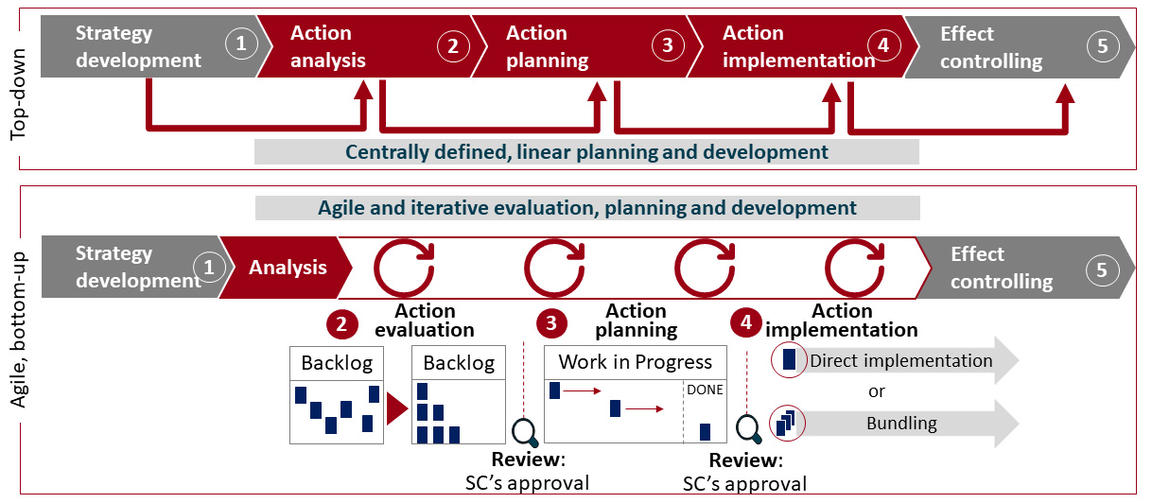
Both the top-down and bottom-up approaches are viable. Choosing the best approach depends on the objectives and framework conditions of the action plan.
acondas NEXT® supports both approaches and ensures stringency and efficiency. Our many years of experience supporting the implementation of efficiency and effectiveness enhancement, cost reduction, growth, innovation, employee and customer satisfaction, and digitization programs equip us with deep expertise in applying proven methods and a wealth of practical implementation experience.
